Augment event data with check hooks
Check hooks are commands the Sensu agent runs in response to the result of check execution.
The Sensu agent executes the appropriate configured hook command based on the exit status code of the check (for example, 1).
Check hooks allow you to automate data collection that operators would routinely perform to investigate observability alerts, which frees up precious operator time. Although you can use check hooks for rudimentary auto-remediation tasks, they are intended to enrich observability event data.
Follow this guide to create a check hook that captures the process tree if a check returns a status of 2 (critical, not running).
Requirements
To follow this guide, install the Sensu backend, make sure at least one Sensu agent is running, and install and configure sensuctl.
The hook you will create in this guide relies on the nginx_service check created in the Monitor server resources guide.
Before you begin, add the sensu/sensu-processes-check dynamic runtime asset and nginx_service check.
Configure a Sensu entity
Every Sensu agent has a defined set of subscriptions that determine which checks the agent will execute.
For an agent to execute a specific check, you must specify the same subscription in the agent configuration and the check definition.
To run the nginx_service check used as an example in this guide, you’ll need a Sensu entity with the subscription webserver.
To add the webserver subscription to the entity the Sensu agent is observing, first find your agent entity name:
sensuctl entity listThe ID is the name of your entity.
Replace <entity_name> with the name of your agent entity in the following sensuctl command.
Run:
sensuctl entity update <entity_name>- For
Entity Class, press enter. - For
Subscriptions, typewebserverand press enter.
Confirm both Sensu services are running:
systemctl status sensu-backend && systemctl status sensu-agentThe response should indicate active (running) for both the Sensu backend and agent.
Install and configure NGINX
The nginx_service check requires a running NGINX service, so you’ll need to install and configure NGINX.
NOTE: You may need to install and update the EPEL repository with sudo yum install epel-release and sudo yum update before you can install NGINX.
Install NGINX:
sudo yum install nginxEnable and start the NGINX service:
systemctl enable nginx && systemctl start nginxVerify that NGINX is serving webpages:
curl -sI http://localhostThe response should include HTTP/1.1 200 OK to indicate that NGINX processed your request as expected:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.20.1
Date: Wed, 06 Oct 2021 19:35:14 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 4833
Last-Modified: Fri, 16 May 2014 15:12:48 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "xxxxxxxx-xxxx"
Accept-Ranges: bytesWith your NGINX service running, you can configure the hook.
Create a hook
Create a new hook that runs a specific command to capture the process tree:
sensuctl hook create process_tree \
--command 'ps aux' \
--timeout 10To confirm that the hook was added, run:
sensuctl hook info process_tree --format yamlsensuctl hook info process_tree --format wrapped-jsonThe response will include the complete hook resource definition in the specified format:
---
type: HookConfig
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: process_tree
spec:
command: ps aux
runtime_assets: null
stdin: false
timeout: 10{
"type": "HookConfig",
"api_version": "core/v2",
"metadata": {
"name": "process_tree"
},
"spec": {
"command": "ps aux",
"runtime_assets": null,
"stdin": false,
"timeout": 10
}
}Assign the hook to a check
Now that you’ve created the process_tree hook, you can assign it to the nginx_service check.
Setting the type to critical ensures that whenever the check command returns a critical status, Sensu executes the process_tree hook and adds the output to the resulting event data.
To assign the hook to your nginx_service check, run:
sensuctl check set-hooks nginx_service \
--type critical \
--hooks process_treeExamine the check definition to confirm that it includes the hook. Run:
sensuctl check info nginx_service --format yamlsensuctl check info nginx_service --format wrapped-jsonYou should find the process_tree hook listed in the check_hooks array, within the critical array:
---
type: CheckConfig
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: nginx_service
spec:
check_hooks:
- critical:
- process_tree
command: |
sensu-processes-check --search '[{"search_string": "nginx"}]'
env_vars: null
handlers: []
high_flap_threshold: 0
interval: 15
low_flap_threshold: 0
output_metric_format: ""
output_metric_handlers: null
pipelines: []
proxy_entity_name: ""
publish: true
round_robin: false
runtime_assets:
- sensu-processes-check
secrets: null
stdin: false
subdue: null
subscriptions:
- webserver
timeout: 0
ttl: 0{
"type": "CheckConfig",
"api_version": "core/v2",
"metadata": {
"name": "nginx_service"
},
"spec": {
"check_hooks": [
{
"critical": [
"process_tree"
]
}
],
"command": "sensu-processes-check --search '[{\"search_string\": \"nginx\"}]'\n",
"env_vars": null,
"handlers": [],
"high_flap_threshold": 0,
"interval": 15,
"low_flap_threshold": 0,
"output_metric_format": "",
"output_metric_handlers": null,
"pipelines": [],
"proxy_entity_name": "",
"publish": true,
"round_robin": false,
"runtime_assets": [
"sensu-processes-check"
],
"secrets": null,
"stdin": false,
"subdue": null,
"subscriptions": [
"webserver"
],
"timeout": 0,
"ttl": 0
}
}Simulate a critical event
After you confirm that the hook is attached to your check, stop the NGINX service to observe the check hook in action on the next check execution.
To manually generate a critical event for your nginx_service check, run:
systemctl stop nginxWhen you stop the service, the check will generate a critical event. After a few moments, run:
sensuctl event listThe response should list the nginx_service check, returning a CRITICAL status (2):
Entity Check Output Status Silenced Timestamp UUID
─────────────── ─────────────── ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── ──────── ────────── ─────────────────────────────── ───────────────────────────────────────
sensu-centos nginx_service CRITICAL | 0 >= 1 (found >= required) evaluated false for "nginx" 2 false 2021-11-08 17:02:04 +0000 UTC xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
Status - CRITICAL Validate the check hook
Verify that the check hook is behaving properly against a specific event with sensuctl.
To view the check hook command result within an event, replace <entity_name> in the following command with the name of your entity and run:
sensuctl event info <entity_name> nginx_service --format yamlsensuctl event info <entity_name> nginx_service --format wrapped-jsonThe check hook command result is available in the hooks array, within the check scope:
check:
...
hooks:
- command: ps aux
duration: 0.00747112
executed: 1645555463
issued: 0
metadata:
name: process_tree
output: |
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
sensu 17638 0.0 0.1 155452 1860 ? R 18:44 0:00 ps aux
...
runtime_assets: null
status: 0
stdin: false
timeout: 10
...{
"check": {
"...": "...",
"hooks": [
{
"command": "ps aux",
"duration": 0.00747112,
"executed": 1645555463,
"issued": 0,
"metadata": {
"name": "process_tree"
},
"output": "USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND\nsensu 17638 0.0 0.1 155452 1860 ? R 18:44 0:00 ps aux\n",
"...": "...",
"runtime_assets": null,
"status": 0,
"stdin": false,
"timeout": 10
}
],
"...": "..."
}
}You can use sensuctl to query event info and send the response to jq so you can isolate the check hook output.
In the following command, replace <entity_name> with the name of your entity and run:
sensuctl event info <entity_name> nginx_service --format json | jq -r '.check.hooks[0].output' This example output is truncated for brevity, but it reflects the output of the ps aux command specified in the check hook you created:
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.3 46164 6704 ? Ss Nov17 0:11 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 20
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Nov17 0:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Nov17 0:01 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Nov17 0:01 [migration/0]
root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Nov17 0:00 [rcu_bh]
root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Nov17 0:34 [rcu_sched]You can also view check hook command results in the web UI.
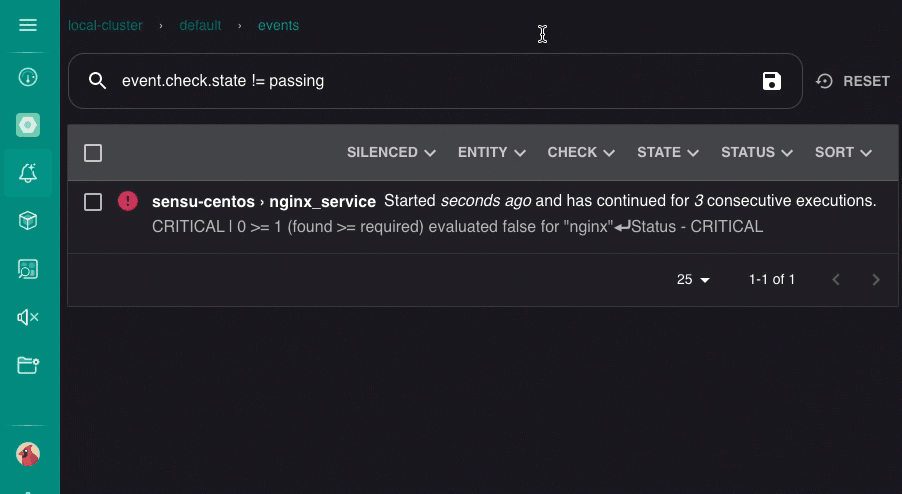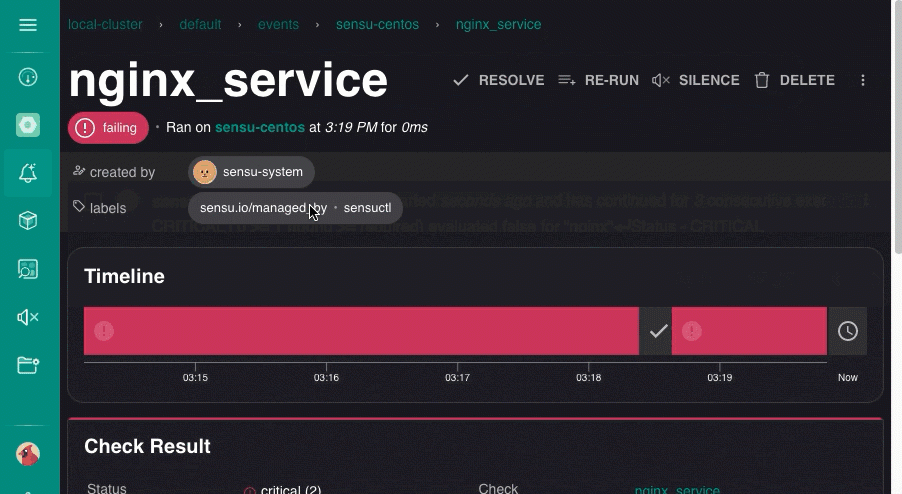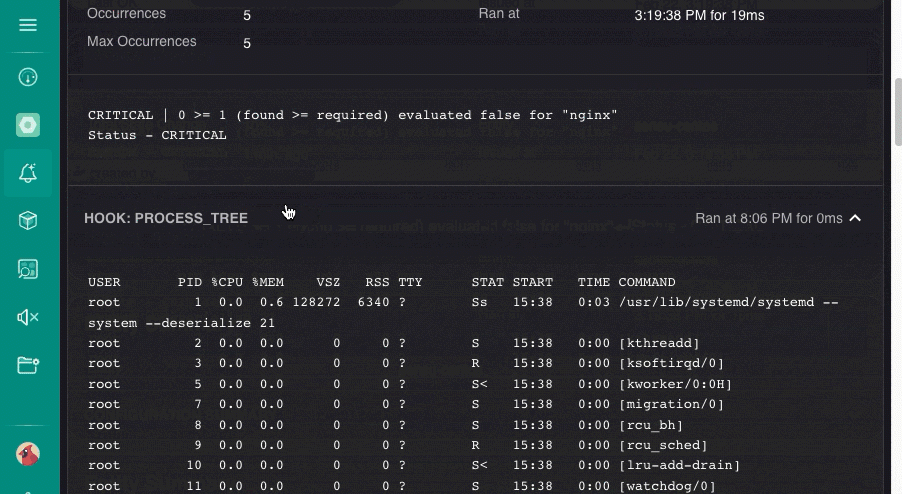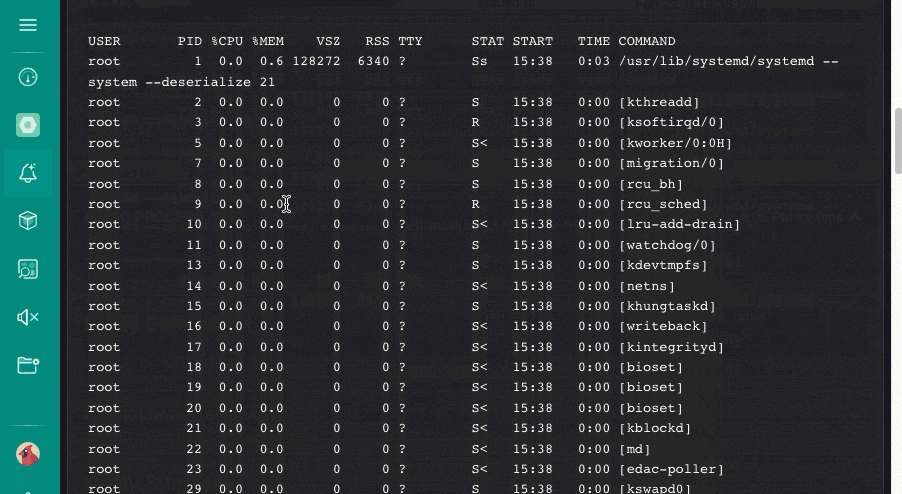
On the Events page, click the nginx_service event for your entity.
Scroll down to the HOOK section and click it to expand and review hook command results.
Restart the NGINX service to clear the event:
systemctl start nginxAfter a moment, you can verify that the event cleared:
sensuctl event listThe response should list the nginx_service check with an OK status (0).
Now when you are alerted that NGINX is not running, you can review the check hook output to confirm this is true with no need to start up an SSH session to investigate.
What’s next
To learn more about data collection with check hooks, read the hooks reference.
Read the subscriptions reference to learn more about Sensu’s publish/subscribe model.
Create pipelines with event filters, mutators, and handlers to send the event data your checks generate to another service for analysis, tracking, and long-term storage. For example:
- Send data to Sumo Logic with Sensu
- Send PagerDuty alerts with Sensu
- Send Slack alerts with a pipeline
In this guide, you used sensuctl to view your check definition, but you can also view complete resource definitions in the Sensu web UI.
